Understanding Multi-Factor Authentication for Better Banking Security
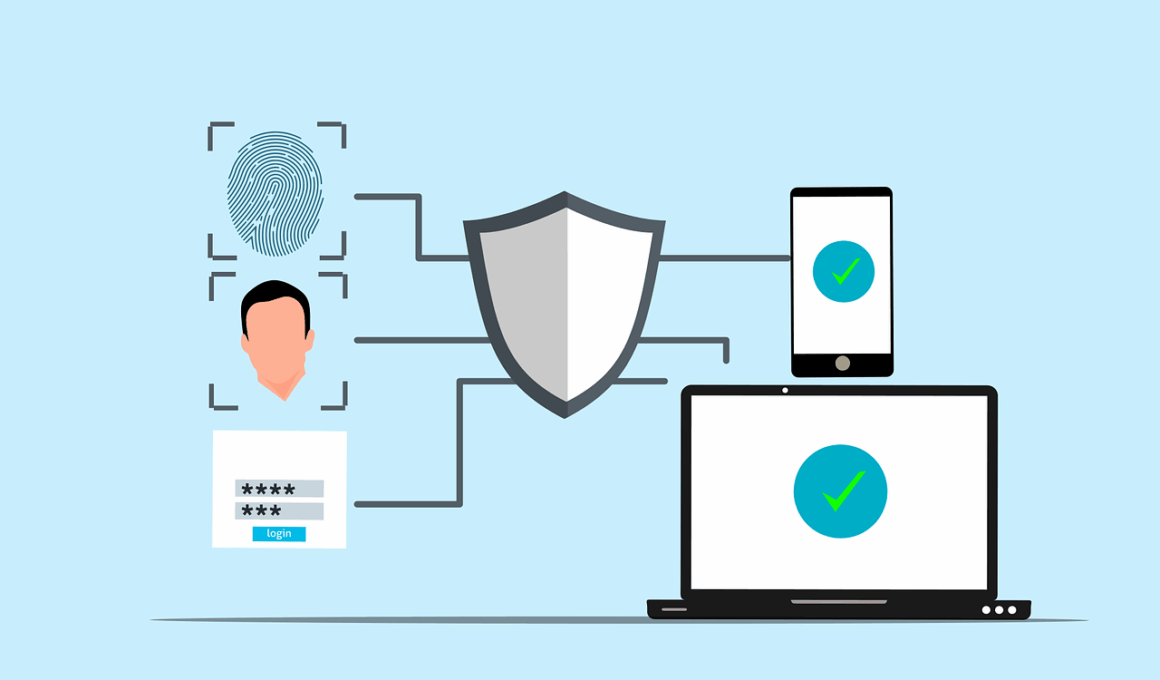
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has become a critical component of secure online banking practices, as financial institutions strive to protect their clients from cyber threats. This process requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to their accounts. Rather than just relying on a username and password, MFA adds layers of security by requiring something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a mobile device), or something the user is (like a fingerprint). This significantly reduces the possibility of unauthorized access. Banks utilize MFA techniques to strengthen their authentication methods, ensuring that customers are aware of potential security risks. With hacks on the rise, methods of authentication that incorporate MFA become a robust defense against identity theft and fraud. Consumers should understand the importance of these practices, which may include text message codes, authentication apps, or biometric scans. Familiarity with MFA not only protects individual financial information but also promotes overall trust in online banking solutions. Customers should take advantage of these security features to help safeguard their accounts from potential threats online.
In addition to using Multi-Factor Authentication, understanding the different types of MFA methods can empower users to make informed choices about their online banking security. These methods can include SMS codes, mobile app notifications, hardware tokens, voice recognition, and biometric methods like facial recognition or fingerprints. Each method provides varying levels of security and usability. For example, while SMS codes are easily accessible, they can be intercepted; however, hardware tokens offer a higher level of security due to their physical form. Users can evaluate their different devices and setup options, based on their preferences for convenience and security. Moreover, banks often update their security measures by introducing new multi-factor strategies to keep pace with emerging threats. Users should remain updated about their bank’s MFA offerings and recommendations. Taking time to select the methods that suit their needs can help account holders feel more secure. Additionally, customers must be informed on how to report any security breaches or suspicious activities immediately. Familiarity with the banking institution’s support tools enhances proactive defense, making a significant difference for safer online banking experiences.
The Role of User Education
Another vital aspect of promoting secure online banking practices is user education regarding Multi-Factor Authentication. Financial institutions have a responsibility to educate their customers on the need to set up MFA options and how to use them correctly. Informing clients about best practices and potential risks associated with lax security measures is essential for fostering a culture of security awareness. Customers should also be encouraged to utilize MFA whenever feasible; failure to do so can leave them vulnerable to attacks. Providing a comprehensive understanding of the workings and implications of MFA can significantly enhance customers’ engagement with these security features. Banks should consider webinars, tutorials, and informative articles that delineate how users can protect their accounts effectively using MFA. Such education can lead to user empowerment, encouraging clients to take an active role in their security. Regular communication between banks and their clients regarding updates in MFA practices contributes to sustained vigilance. It’s essential that financial institutions not only implement technologies but also ensure that consumers fully understand the tools at their disposal for better security.
Moreover, the implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication aligns with regulatory standards, making it a mandated practice in many financial organizations. Depending on their specific jurisdiction, financial institutions may be required to adopt MFA as part of compliance with various laws and regulations. Regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), emphasize the need for strict security measures to prevent data breaches and other security risks. Compliance reinforces the idea that financial institutions must prioritize their customers’ safety above all else. Adopting MFA not only helps comply with regulatory expectations but also builds trust among customers. Clients are more likely to continue banking with institutions that prioritize secure practices and provide transparent information on protective measures. Thus, banks participating in regular security audits and assessments are ensuring that their systems are updated consistently to meet both the safety needs of users and regulatory mandates. In the evolving landscape of cyber threats, consistent adherence to established security practices, including MFA, serves as a critical step for building a secure online banking environment.
Challenges in Implementation
Despite the overwhelming benefits of Multi-Factor Authentication, several challenges complicate its widespread implementation in online banking. One significant hurdle is user resistance to adopting more complex authentication processes, especially if these practices disrupt their traditional banking habits. Users accustomed to simple login methods may find MFA inconvenient and may ignore or opt-out of using it. Additionally, banking institutions face technical challenges when integrating MFA into their existing infrastructure. Compatibility issues may arise with older systems, leading to potential disruptions. Tech-savvy hackers can also exploit weaknesses in these systems, making it crucial for banks to invest in modern cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information effectively. Furthermore, banks must cater to a diverse customer base, which includes individuals who may encounter difficulties with technology. Education is paramount in addressing these hurdles; providing clear instructions and support can alleviate user frustrations with new processes. Therefore, tailoring approaches to user needs enhances overall security while minimizing barriers to MFA adoption. Financial institutions should proactively address these issues as they implement strong authentication methods.
Furthermore, as the world transitions into a more mobile-centric lifestyle, the relevance and prevalence of Multi-Factor Authentication continue to grow significantly. Mobile banking applications are widely used, making it imperative for service providers to integrate MFA into their platforms seamlessly. The use of biometric authentication, such as facial recognition or fingerprint scans, has gained popularity among users, demonstrating heightened flexibility without compromising security. These modern approaches are not only convenient but also help to streamline user experiences while ensuring sensitive financial information is protected. As customers engage increasingly with mobile devices for banking transactions, it is vital for financial institutions to continually innovate their authentication methods to keep pace with user expectations. The development of new technologies will usher in enhanced security protocols, pushing the boundaries of traditional MFA practices. Customers should stay informed about these advancements to take advantage of enhanced security features. Above all, as clients embrace new technologies, they must remain vigilant about online safety and the importance of employing multi-factor authentication to protect financial resources effectively.
Looking Ahead
As we look into the future of online banking security, Multi-Factor Authentication will undoubtedly evolve to meet the challenges presented by emerging cyber threats. Continuous advancements in technology will facilitate more sophisticated measures for verification that are user-friendly yet robust against attacks. Companies are exploring new trends, including behavioral authentication which analyzes user patterns to verify identities. This next generation of MFA will rely on artificial intelligence and machine learning to adapt to user habits, providing an even greater layer of security. Meanwhile, regulatory and compliance frameworks will likely expand to ensure that banks continue to safeguard their clients’ information. Collaboration between banks and tech innovators will be key in creating efficient, secure, and user-centric solutions. Furthermore, ongoing consumer education will remain a pillar of secure online banking practices. Clients equipped with knowledge about how to utilize MFA tools effectively will enjoy greater peace of mind. By embracing change and remaining vigilant against threats, both banks and customers can strategically prepare for a safer online banking future. Ultimately, the focus on multi-layered security remains paramount in the fight against cybercrime.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing Multi-Factor Authentication plays a crucial role in enhancing online banking security. With cyber threats evolving and becoming more sophisticated, it is essential for both banks and users to prioritize MFA as a fundamental aspect of secure online transactions. Banks must take the lead in educating customers about MFA, demonstrating its importance, and encouraging its usage as a first line of defense against identity theft and fraud. Clients must also recognize their role in safeguarding their financial information by adopting these robust security measures. By embracing these practices, a collaborative effort can be established to combat cyber risks that threaten the integrity of online banking. Expecting that the banking sector will continue to innovate security technologies, customers should be proactive in staying informed about new MFA strategies. They should continually assess their security practices and collaborate with their financial institutions to enhance their safeguards. In a world where digital transactions are commonplace, understanding and utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication will significantly improve overall security and foster a more secure banking environment for everyone. Together, these efforts will contribute to a more robust and trustworthy online financial landscape.