Economic Development Through Export-Oriented Industrialization
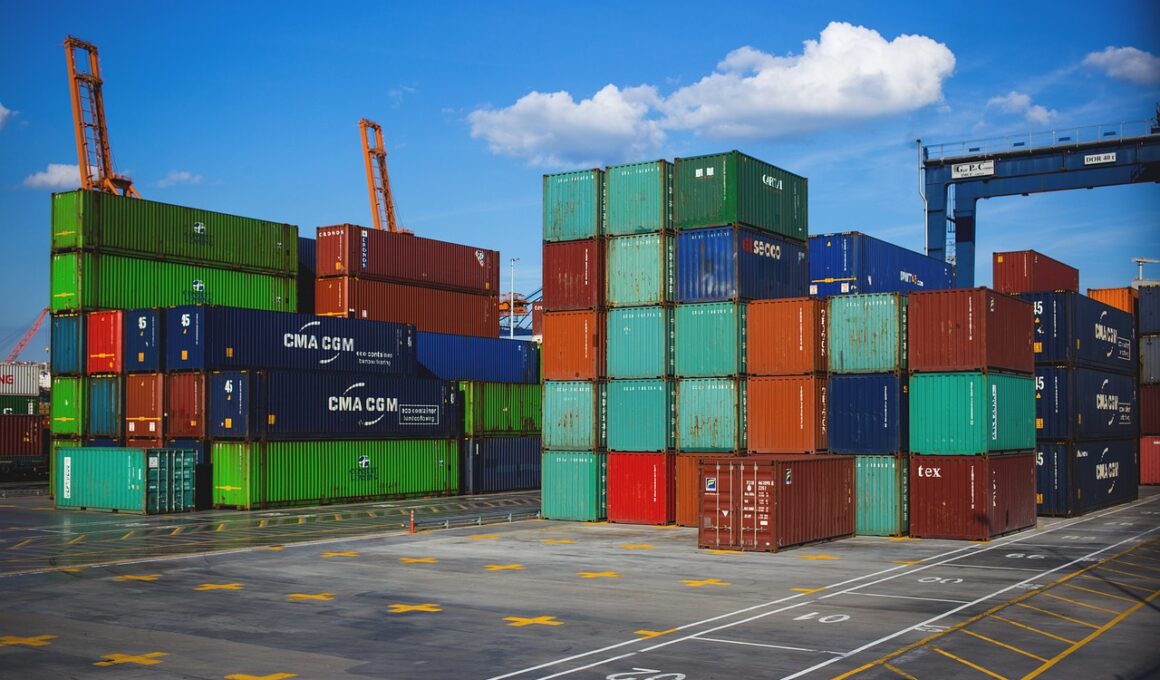
Export-oriented industrialization (EOI) is an economic strategy that aims to accelerate a country’s economic development by concentrating on the production of goods for export. Many countries have employed this model successfully, leading to significant improvements in employment, income levels, and technological advancement. The driving force behind EOI is the ability to tap into international markets, which encourages domestic industries to produce competitively priced and high-quality products. By focusing on exports, governments can stimulate economic growth, enhance foreign exchange earnings, and reduce trade deficits. Additionally, EOI can attract foreign direct investment (FDI) that brings capital and technology into countries, fostering industrial growth. Strategies often include establishing special economic zones (SEZs) to create favorable conditions for businesses. However, the implementation of EOI requires comprehensive policies that address labor standards, environmental regulations, and trade agreements to ensure sustainable development. Furthermore, countries must invest in infrastructure, education, and skills training to prepare their workforce for changing demands. The intersection of global trade frameworks and local economic policies is where EOI becomes a powerful tool for development, offering a pathway to a more competitive economy.
Countries embarking on export-oriented industrialization often encounter significant challenges. While the potential benefits are substantial, the journey requires a series of strategic decisions that foster industrial growth. One primary hurdle is ensuring that local industries can compete globally; this involves upgrading technology and improving productivity. Governments play a crucial role in this transition by offering incentives such as tax breaks, subsidies, or investment in infrastructure to support emerging industries. Moreover, it is vital to establish robust trade policies that both protect and promote local goods in international markets. Trade agreements can help to liberalize markets, reducing tariffs on exports and enhancing market access for local firms. Additionally, nurturing partnerships between government, businesses, and educational institutions can create a skilled workforce ready for export industries. Companies must align their production with global demand, emphasizing quality and innovation. A successful EOI strategy must also incorporate feedback loops where industry players can communicate their needs and challenges. Therefore, fostering an adaptive regulatory environment encourages innovation while promoting sustainable practices that align with international standards, resulting in a thriving export sector.
The Role of Government in EOI
A well-defined government policy framework is crucial to the success of export-oriented industrialization. Effective policy interventions can help foster a favorable business climate for local industries while facilitating access to international markets. Governments must prioritize investments in infrastructure such as transportation, communication, and energy systems to reduce operational costs for exporters. In addition, enhancing logistics and supply chains ensures that goods can be efficiently produced and delivered to consumers globally. Furthermore, targeted financial support can be offered to specific industries that show the potential for exports, such as technology, textiles, or agriculture. Governments can also facilitate the presence of trade advisors who assist businesses in navigating export processes and regulations. Another crucial aspect is the development of clusters of industries that collaborate to share resources, knowledge, and skills, enabling faster innovation and adaptation. Through public-private partnerships, governments can leverage private sector capabilities to enhance productivity and competitiveness. Regular assessments of policies must be conducted to measure their effectiveness and adapt strategies that align with changing global market conditions, ensuring that the benefits of EOI are sustained over time.
In today’s globalized economy, trade agreements are instrumental in promoting export-oriented industrialization. Various regional and bilateral trade agreements have been established to facilitate easier access for exporting countries. These agreements often reduce tariffs and non-tariff barriers, creating an enabling environment for industries to thrive. Countries participating in these agreements benefit from increased trade volumes, exposure to new markets, and opportunities for collaboration. Engaging in trade blocs can lead to larger market penetration, allowing nations to increase their export capabilities significantly. Furthermore, trade agreements often come with stipulations that protect workers’ rights and the environment, ensuring that the path to economic growth is responsible and inclusive. However, it is essential for countries to actively negotiate terms that are favorable to their industries while not sacrificing domestic interests. The importance of aligning these agreements with national development strategies cannot be overstated, as they must complement domestic policies designed to foster sustainable and equitable growth. To summarize, trade agreements serve as catalysts that enable countries to pursue export-oriented industrialization effectively, boosting overall economic development through increased global participation.
Challenges in EOI Implementation
Despite the potential benefits of export-oriented industrialization, several challenges can impede progress. One major issue is the reliance on external markets, which can expose countries to global economic fluctuations and trade disputes. A downturn in key export markets can lead to significant revenue losses, triggering economic instability. Additionally, countries may become overly dependent on a limited range of exports, which can hamper diversification efforts and make economies vulnerable. Furthermore, sectors involved in exports may struggle to attract skilled labor due to competition with other industries, thereby limiting growth. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that includes investment in research and development, promoting entrepreneurship, and encouraging innovation across various sectors. Diversifying export products and markets can mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on specific goods or regions. Strengthening domestic demand can also provide a buffer against external shocks, ensuring economic stability. Ultimately, while EOI offers a promising pathway to development, its implementation involves navigating complexities that necessitate careful planning and robust frameworks to sustain progress.
Export-oriented industrialization can have profound impacts on social structures within countries pursuing this strategy. By focusing on expanding industries, EOI has the potential to create a significant number of jobs, lifting many families out of poverty. However, the nature of these jobs often varies; thus, it becomes essential to ensure that employment is decent, equitable, and inclusive. Providing workers with fair wages and safe working conditions enables them to participate meaningfully in economic growth. Moreover, fostering gender equality in the workforce can further enhance productivity and social stability. Integrating marginalized groups into the labor market is a critical consideration for equitable development. As local industries grow, investing in education and training programs is vital to ensure that the workforce can adapt to changing demands and leverage new technologies responsibly. Escaping the cycle of poverty not only benefits individuals but also leads to improved social cohesion over time. In this context, successful EOI contributes to a larger narrative of sustainable development, where economic activities enhance the overall quality of life for all segments of society.
Conclusion
In conclusion, export-oriented industrialization presents both opportunities and challenges as a strategy for economic development. When effectively implemented, EOI can foster significant industrial growth, job creation, and technological innovation, positioning countries favorably in the global marketplace. Governments play an essential role in curating robust policy frameworks that prioritize infrastructure development and support local industries while facilitating access to international markets through trade agreements. The importance of diversifying exports and creating skilled workforces cannot be understated, as these elements mitigate vulnerabilities related to global market fluctuations. Addressing social aspects ensures that economic growth translates into higher living standards and equitable opportunities for all citizens. Ultimately, the path toward export-oriented industrialization must be navigated with planning and foresight, incorporating stakeholder feedback to evolve strategies ensuring long-term sustainability. Through a comprehensive approach that includes government, industry, and society, countries can harness the full potential of EOI to drive economic growth and achieve a more prosperous future.