How Technology Transfer is Reshaping the Manufacturing Sector in Global Trade
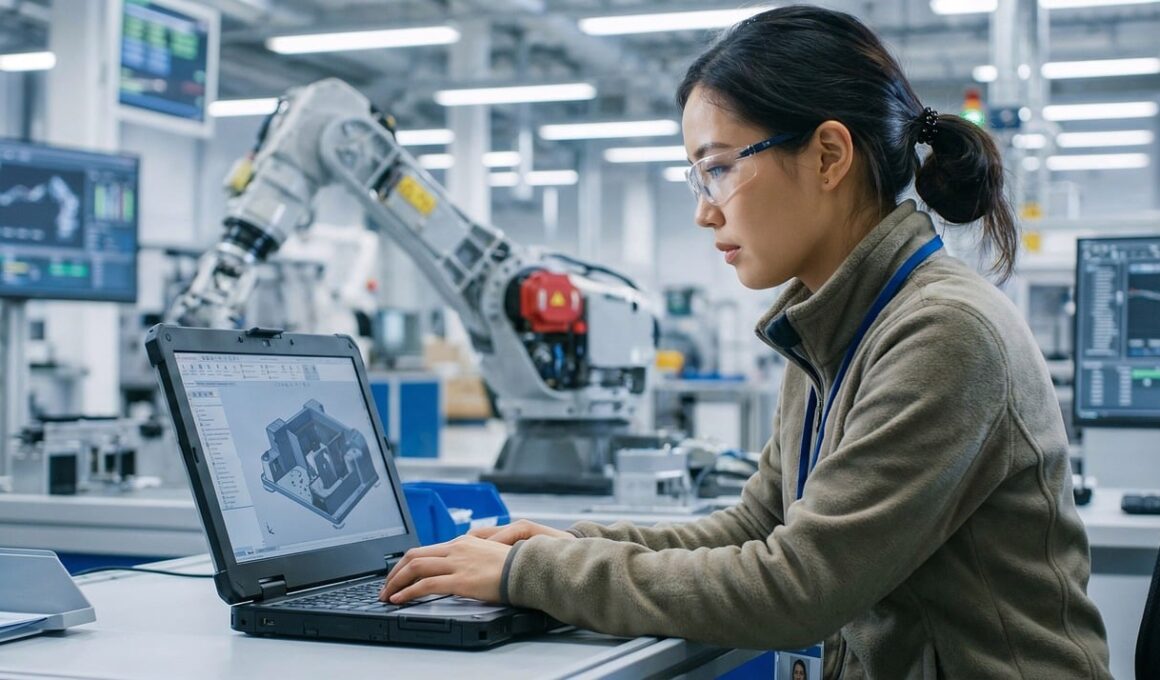
In recent years, the manufacturing sector has undergone significant transformation, driven by the rapid advancement of technology. Global trade has become increasingly interconnected, and technology transfer is at the forefront of this change. Companies worldwide leverage modern technologies to improve efficiency, productivity, and ultimately, competitiveness. Such technologies range from automation and robotics to artificial intelligence and data analytics. As firms adopt these innovations, the barriers to entry for new players diminish, enabling more businesses to join the trade ecosystem. Moreover, technology transfer enhances collaboration among nations, fostering a more dynamic global market. The integration of advanced technologies allows firms to streamline operations and optimize supply chains, leading to reduced costs and faster delivery times. As a result, firms that embrace technology transfer can respond swiftly to market demands. This responsiveness is vital in a landscape characterized by rapid shifts in consumer preferences and economic conditions. Consequently, technology transfer not only transforms individual businesses but also reshapes entire industries, creating opportunities for growth and development across the globe.
The importance of technology transfer cannot be overstated, especially in manufacturing. As industries become more global, companies are increasingly seeking advanced technologies to stay competitive. Without technology transfer, businesses risk falling behind their rivals who may have access to cutting-edge innovations. For developing countries, technology transfer plays a crucial role in industrialization. It provides access to knowledge and technologies that can uplift their manufacturing capabilities significantly. Additionally, established firms in developed nations often engage in partnerships with startups in emerging markets to facilitate this transfer. Such collaborations enable the sharing of best practices, R&D initiatives, and technical know-how, creating a robust ecosystem for innovation. Moreover, technology transfer helps in expanding the potential for product development and diversification. For instance, firms can innovate on existing products or create entirely new offerings by leveraging transferred technologies. This leads to increased market competition and can benefit consumers. Overall, the continuous flow of technology between countries fosters economic growth, reduces inequality, and encourages sustainable development. To maximize these benefits, stakeholders must actively participate in and support technology transfer initiatives within their respective sectors.
Impact on Trade Dynamics
Technology transfer has profound implications for trade dynamics in today’s economy. It influences how countries position themselves in the global market and affect trade relations. As companies adopt innovative technologies, they can produce high-quality goods at a lower cost. This increase in quality and efficiency can lead to a more competitive edge internationally and better export opportunities. Firms that actively engage in technology transfer are better equipped to adapt to changing global supply chains. Additionally, technology enables manufacturers to comply with international standards and regulations, further enhancing their export potential. With improved operational capacity, businesses can tap into new markets and respond to global demand trends. The evolution of trade agreements often incorporates elements related to technology sharing, aiming to encourage collaboration between nations. Through such frameworks, countries can secure favorable terms for the exchange of technology. Moreover, countries investing in education and skills development ensure a workforce capable of leveraging these technologies effectively, fostering a knowledgeable environment. This strategic alignment is critical for nations hoping to enhance their global competitiveness and participation in international trade networks.
In the context of international trade, technology transfer can also address challenges related to sustainability. As nations strive to meet environmental standards, adopting green technologies becomes essential. Companies involved in technology transfer often implement sustainable practices, leading to reduced waste and energy consumption. This capability not only benefits the environment but also improves profitability through cost savings. For instance, industries investing in renewable energy technologies can dramatically cut operational costs and enhance their brand image. Consequently, firms become more attractive to consumers who prioritize environmentally friendly practices. Furthermore, governments are incentivizing technology transfer initiatives that focus on sustainability through policies and grants. This alignment of economic and ecological interests benefits society at large and enhances resilience against climate change. By embracing eco-innovations, firms can differentiate themselves in a crowded market, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Ultimately, technology transfer can play a pivotal role in facilitating the shift towards sustainable manufacturing practices on a global scale, reflecting a broader commitment to responsible trade and production strategies that benefit both people and the planet.
Challenges and Risks Associated
Despite the clear advantages, technology transfer in manufacturing comes with inherent challenges and risks that stakeholders must navigate. Security concerns often dominate discussions surrounding technology transfer, particularly when sensitive data or proprietary technologies are involved. Companies need to establish robust protections to safeguard intellectual property during the transfer process. Additionally, there is the risk of technological dependency, where nations or businesses may rely excessively on foreign technologies, potentially stifling local innovation. As a result, developing home-grown capabilities is crucial. Furthermore, cultural and operational differences can pose barriers to effective technology transfer. Each organization has its own practices, and aligning these can be challenging. To mitigate such risks, firms must adopt comprehensive strategies that encompass effective knowledge transfer protocols, training, and continuous support. Strong leadership and commitment from all parties enhance these efforts, ensuring that technologies are assimilated seamlessly into the existing operational framework. By addressing these challenges proactively, stakeholders can maximize the benefits of technology transfer in the manufacturing sector while minimizing potential downsides that may arise.
Furthermore, the impact of technology transfer on workforce dynamics cannot be overlooked. As firms adopt advanced technologies, the nature of work within the manufacturing sector is evolving. While automation may improve efficiency, it also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for upskilling existing employees. Companies must invest in training programs to ensure their workforce is prepared for the new technological landscape. This investment not only benefits employees but also enhances the organization’s overall productivity. A well-trained workforce can leverage advanced tools and processes effectively, leading to better outcomes. Moreover, as new technologies emerge, new roles and opportunities will arise within the industry, creating pathways for growth and development. However, addressing the skills gap requires cooperation between governments, educational institutions, and the private sector. By collaborating, stakeholders can develop targeted training initiatives that align with industry needs, ensuring preparedness for the future. Consequently, the successful implementation of technology transfer relies not just on technological advancements, but also on a proactive approach towards developing human capital in the manufacturing sector.
The Future of Technology Transfer
Looking ahead, the future of technology transfer in the manufacturing sector appears promising yet unpredictable. The continuous evolution of advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain presents both opportunities and challenges for global trade. As these technologies become more integrated into manufacturing processes, the pace of innovation is likely to accelerate. Companies that are agile in adopting and transferring new technologies will be better positioned to thrive in this dynamic environment. Furthermore, a collaborative approach among nations will be essential to facilitate knowledge sharing and foster innovation clusters. Governments worldwide may need to rethink their policies and frameworks to accommodate the rapid changes in technology landscape. This may include creating incentives for technology acquisition and pushing for transparency in technology transfer agreements. Additionally, ethical considerations will come to the forefront, especially regarding data privacy and security in technology sharing. Stakeholders must navigate these complexities with accountability and foresight. Ultimately, the goal should be to create a balanced ecosystem where technology transfer can drive manufacturing excellence while ensuring sustainable and equitable growth across borders.
In conclusion, technology transfer is a key driver reshaping the manufacturing sector in global trade. The integration of modern technologies enhances business competitiveness, fosters sustainable practices, and facilitates positive workforce dynamics. However, it also presents challenges that must be managed carefully, including security risks and the need for upskilling employees. By addressing these issues proactively, stakeholders can unlock the full potential of technology transfer. Future developments in this dynamic field will likely demand increased collaboration among nations and innovation partnerships across industries. With an evolving global landscape, companies must remain adaptable and forward-looking. The successful implementation of technology transfer initiatives will not only benefit individual businesses but will also contribute to broader economic growth and prosperity worldwide. As nations continue to prioritize technological advancements, they must ensure that such progress is inclusive, sustainable, and equitable. By embracing this transformative force, stakeholders can enhance their capabilities and strengthen their positions in the competitive manufacturing landscape of tomorrow.