The Role of Moving Averages in Technical Trading
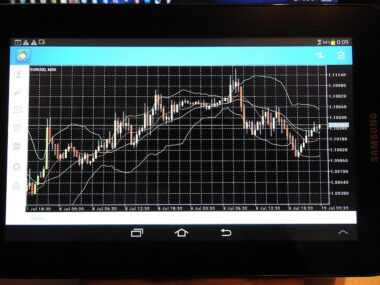
Moving averages are essential tools in the world of technical analysis, providing traders with insights and simplifying complex data into understandable trends. These averages allow analysts to smoothen price data over a specific period, facilitating the identification of trends. Essentially, a moving average can help eliminate noise in price fluctuations, making it easier for traders to spot continuities or reversals. There are various types of moving averages, with the two most common being the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA). Each type has its unique methodologies, influencing the weight of data points differently. For instance, the SMA calculates the average price over a set number of periods, whereas the EMA gives priority to more recent prices. This results in the EMA being more sensitive to recent price movements. Using these moving averages, traders can make more informed decisions on when to enter or exit positions based on the signals they produce in combination with other indicators. Ultimately, a well-implemented moving average strategy can contribute significantly to a trader’s overall market assessment.
Types of Moving Averages
A comprehensive understanding of the different types of moving averages is crucial for effective trading. The two primary forms are the simple moving average (SMA) and the exponential moving average (EMA), each serving distinct trading purposes. The SMA is straightforward; it simply averages the prices over a set number of time periods, providing a clear viewpoint of average price movement. Conversely, the EMA weighs the most recent prices more heavily, reacting swiftly to price movements and offering earlier signals compared to the SMA. There are also weighted moving averages (WMA), which assign varying weights to each price within a given period. Moving averages can also be combined, such as in the common crossover strategy, where traders watch for the intersection of the short-term and long-term moving averages. This interaction can generate buy or sell signals, making it a favored approach in technical trading. For traders focusing on trend analysis, understanding these various types not only sharpen instincts but also empowers them to make more calculated decisions in fast-moving markets.
The significance of trend direction becomes evident when using moving averages in technical analysis. The basic premise behind moving averages is their ability to reveal the direction of market trends. When prices are above a moving average, it commonly suggests an upward trend, while prices below indicate a downward trend. This visual representation helps traders quickly determine market sentiment and adjust their strategies accordingly. Furthermore, moving averages can act as dynamic support and resistance levels. When the price approaches the moving average from above, traders may view it as a potential support level and, conversely, a resistance level from below. This dual function further solidifies the importance of moving averages in trading decisions. Additionally, the distance between the price and the moving average can provide insights into market volatility. Larger gaps may indicate stronger trends, while smaller ones could suggest market indecision. Integrating moving averages into a trading strategy can simplify analyses and lead to better-informed decisions when navigating complex market dynamics.
Crossovers: A Key Technique
One of the most effective techniques in utilizing moving averages for trading is the crossover strategy. This method relies on the interaction between two moving averages, typically one short-term and one long-term. A crossover occurs when a short-term moving average crosses above or below a long-term moving average. A bullish signal is generated when the short-term average crosses above the long-term average, indicating a potential buy opportunity. Conversely, a bearish signal occurs when the short-term average crosses below the long-term average, suggesting it may be time to sell. This simplicity makes the crossover technique popular among traders. Moreover, traders often employ multiple time frames to confirm trends and validate signals generated by the moving averages. For example, a trader might analyze a 50-day SMA in conjunction with a 200-day SMA to identify potential long-term trend changes. This multi-dimensional approach not only increases accuracy but also enhances confidence in making trading decisions. Properly executed, crossover strategies can prove to be both powerful and efficient in capturing profitable trades.
As with all trading strategies, the use of moving averages is not without its limitations. False signals can emerge, particularly in volatile markets where rapid price changes can mislead traders. Additionally, lagging indicators such as moving averages may not provide timely signals in rapidly changing market conditions. It’s vital for traders to complement moving averages with other indicators and tools, such as momentum oscillators or trend indicators, to maximize their effectiveness. Analyzing the bigger market picture—using news events, economic indicators, and other factors is also key. Understanding the market context can help traders interpret the signals generated by moving averages more accurately. Furthermore, the settings for the moving averages must be tailored to match a trader’s specific objectives and timeframes. Customizing parameters according to the trading style can enhance the moving average’s effectiveness. Therefore, continuous review and adjustment of these parameters are advisable for maintaining accuracy over time and ensuring consistency in trading performance.
Combining Moving Averages with Other Indicators
To enhance the effectiveness of moving averages in technical trading, combining them with other indicators is a common practice. Technical traders frequently integrate moving averages with oscillators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). Oscillators can provide additional context to the signals generated by moving averages, aiding in the identification of overbought or oversold conditions. For instance, a bullish crossover confirmed by a MACD signal can offer more confidence in the validity of the trade. Furthermore, using Fibonacci retracements in conjunction with moving averages can highlight key support and resistance levels for more precise entry and exit points. This multidimensional strategy not only provides a holistic view but also enhances the probability of success. However, traders should remain cautious and avoid overloading their charts with too many indicators, as this can lead to analysis paralysis. Instead, focusing on a few complementary indicators allows traders to establish a clearer trading strategy, leading to more informed and disciplined decisions.
The successful application of moving averages in trading requires continuous learning and adaptation. Market conditions constantly evolve, as do the effectiveness and relevance of different moving average strategies. Traders need to consistently refine their approaches based on performance, market response, and personal trading style. Backtesting strategies on historical data can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of moving averages in various market conditions. Documenting trades and analyzing outcomes is also crucial for improvement and growing proficiency. Continuous assessment allows traders to determine which periods work best for their chosen moving averages and when adjustments are necessary. Moreover, regular education through industry resources, seminars, blogs, or mentorship can significantly impact a trader’s success. Embracing a mindset of adaptability and lifelong learning will serve traders well in the often unpredictable realm of technical analysis. By staying informed and continuously refining strategies, traders can navigate the complexities of the market more effectively, leveraging moving averages to enhance their trading performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, moving averages play a vital role in technical analysis for traders. Their ability to simplify complex market data allows traders to identify trends and make informed decisions more effectively. While moving averages have their limitations, combining them with other indicators can amplify their power. The crossover strategy serves as an excellent example of how to apply moving averages to establish market entry and exit points. Learning to adapt moving averages to fit personal trading styles is necessary for maximizing their benefits. Continuous education and a focus on market dynamics will ensure that traders can successfully navigate the financial landscape. Moving averages are not just tools but gateways to understanding market behavior and enhancing overall trading strategies. By implementing thorough analysis rooted in moving averages, traders can better position themselves for success. Ultimately, gaining a firm grasp of moving averages can greatly benefit traders looking to excel in technical trading.